On Thursday, May 27th, key players from the haptics, hand tracking, and VR training industries gathered to discuss the scaling of haptics in VR training applications. It addressed how a company can leverage haptic technology across all their virtual training scenarios thanks to Interhaptics and Innoactive technologies.
Interhaptics allows the creation of great virtual reality haptics scenarios in a few clicks with the integration of exoskeleton and haptics gloves into the scalable enterprise VR training roll-out solution, the Innoactive creator. All actors of the value chain, from the software development with Interhaptics and Innoactive to hardware manufacturers with SenseGlove, ManusVR, and Sensoryx.

VR Training defines a solution using virtual or mixed reality to transfer useful skills to the trainee. Enhancing the user experience is key in VR Training, but controllers can be very limiting for this kind of experience. Haptic gloves and exoskeletons represent real game-changers when it comes to VR Training. They significantly increase the added value, user experience, and efficacity of the training. The development of high-fidelity hand tracking interactions and haptic feedback can take a very long time and be complicated. This article will go through the best examples of implementing haptics to exoskeletons and gloves.
Main points of the webinar
The National Education Association of the United States conducted a study about the different learning retention rates depending on the most common learning methods available today.
Learning retention refers to the process by which new information is transferred from short-term memory to long-term memory. In other words, it essentially involves gaining new knowledge.
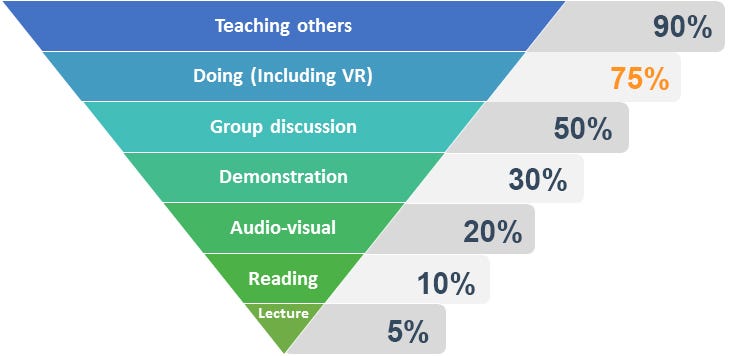
In this diagram, we can see that lecture and reading methods, which are commonly used, also have the lowest rates. Audio-visual, which is used more and more for traditional training, comes in the third position with a learning rate of 20%. However, we can see that the rate for VR Training is very high, at 75%. Showing that, by allowing your trainee to do exercises by themselves with the help of virtual technologies, you drastically improve the efficiency of your training.
Scalability process of haptics
VR training is a very strategic area for VR companies in the market. It can be easily explained by data from a case study made by Innoactive, Unity, and Volkswagen. VR training was found to reduce training time by 50%, and with only a third of the training costs. It was also very highly recommended by the users.

Founded in 2013, Innoactive is a leading provider of enterprise VR solutions based in Munich. They offer an open VR training platform that enables an efficient roll-out of VR training globally. Their modular set of software tools and web services allow the VR training app development and deployment to be scalable.

The scaling process can be divided into “boxes,” from creation to deployment, between Unity, Interhaptics, and Innoactive. The creator is integrated with the Interhaptics development tool directly into Unity to design haptic-enabled VR training content without writing code. Haptics assets created with the Haptic Composer can be used during the process. It can then be deployed on any devices like the ManusVR, SenseGlove, and Sensoryx. The Innoactive portal allows the deployment of the content on different technologies.
Thanks to Interhaptics, haptic feedback can be deployed both for controllers and haptic devices. This offers great scalability of the content creation process as well as the development process.
Uses Cases and Best Practices
Procedural training
Aerospace is one of the sectors where VR Training is most relevant because you do not want to replicate an entire cockpit due to its very high cost. And even if an airline or aviation companies have the resources to invest in this type of training, there are two different kinds of issues:
- First, the simulation cockpits are used 24/7 and present a lack of technology,
- Second, they are made only to replicate the most important tasks and cannot provide a wider basis.
Indeed, this use case presents Sensoryx VR Free gloves, which offer cost-efficient and seamless integration into existing applications for hand and finger tracking. There is no need to have an extra tracking solution to know exactly where the hands are and what they are doing, even if they are not in the direct line of sight. It comes in very handy for pilot training and civil airplane training.
This use case was created for a Dutch company. It is based in a restaurant, and the user has to complete an order. He has to grab certain items and place them on the tray, and if he does anything wrong, the experience notifies him. This use case was created to train neurological patients for entry back into the working world so they could work again. Their handling of the order is tracked to ensure they are doing the different steps, checking the things they grab first and the mistakes they might make so their improvements can also be tracked.

Another B2B use case is for assembly line training. The user can learn how to do a specific task. In this case, it is important to have a mobile training system. It also means that you can personalize the tasks you want each employee to be trained on.
High-risks training
The first use case is from Telexistence, a Japanese company that created a robot (Model H) completely reproducing the actions of the user controlling it. They created an immersive and accurate experience. Using the gloves and the headset, the user could be present somewhere they would not usually be. The user can also see through the robot’s eyes. The arms of the robots are articulated, thanks to SteamVR trackers, to push the immersion experience a step further. Telexistence created this using ManusVR C++ SDK and added their force feedback modules.
The next use case was created for the Dutch army and allow the students to virtually train to avoid damaging real equipment. Indeed, it drastically reduces the costs. They already had a VR training solution, but they were looking for a mobile device with a higher feedback fidelity and not just for motion capture.
This use case was made for Volkswagen and again shows the importance of force feedback. There are many detailed interactions inside this particular assembly training of a door panel of a van model. This VR training is a digital equivalent to a physical mock-up.
One important thing to remember is that haptics cannot miraculously physically mimic real-world textures to the point where you can distinguish skin and wood.
If you have a VR training project and are interested in collaborating with any of the companies present during this webinar, you can contact us using this form.

Introduction to Interhaptics
Interhaptics is a software company specialized in haptics. Interhaptics provides hand interactions and haptic feedback development and deployment tools for virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MR), mobile, augmented reality (AR), console applications, and the interoperability of haptics-enabled content across any haptics-enabled platform. Interhaptics’ mission is to enable the growth of a scalable haptics ecosystem.
You want to develop a training scenario in VR with Interhaptics? Read this article to find out more.
If you are interested in collaborating with Interhaptics for creating a POC, contact us here.






